We compared Cohere v3.5 and ZeRank-1 to see which reranker performs better inside a RAG pipeline. Tests ran on a private dataset and a BEIR/FIQA subset.
TL;DR
ZeRank ranks higher on nDCG and Recall and is favored by the LLM in 39 out of 50 cases, while Cohere is faster on average and steadier under load.
What We Found
Accuracy
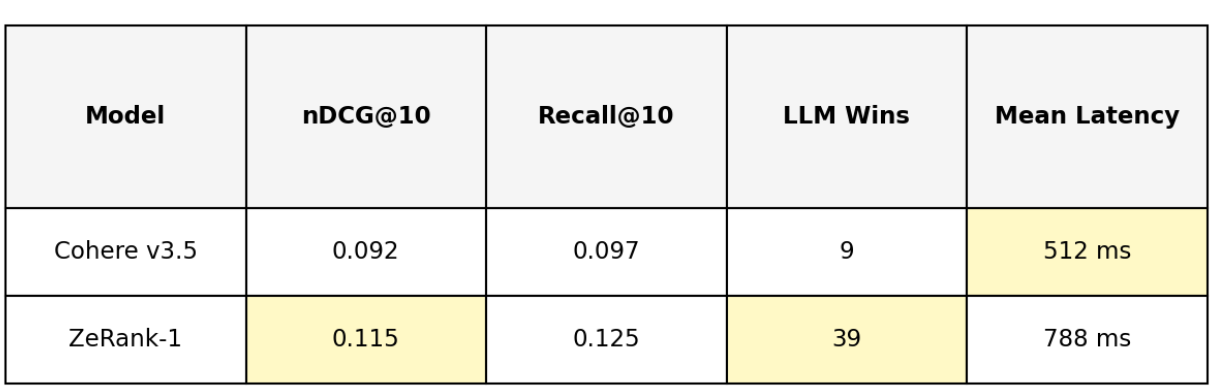
Across both datasets, ZeRank achieved higher nDCG and Recall@k (k = 5, 10). The difference grows slightly as k increases, showing stronger ranking depth.
Latency
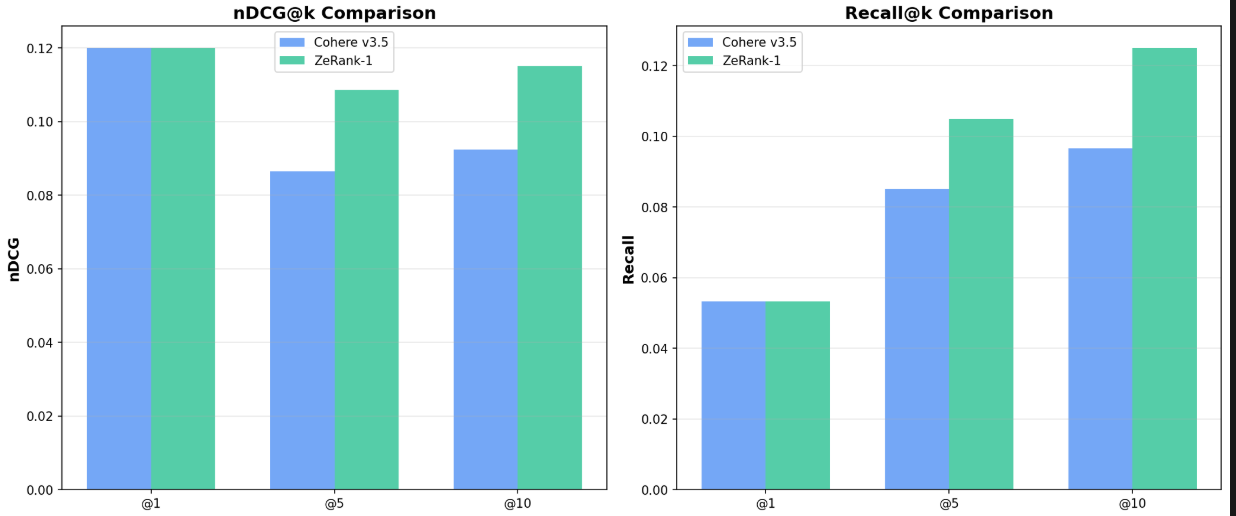
Cohere had lower mean and p90 latency, making it more consistent under load, while ZeRank responded faster on typical queries (lower p50).
LLM judgment
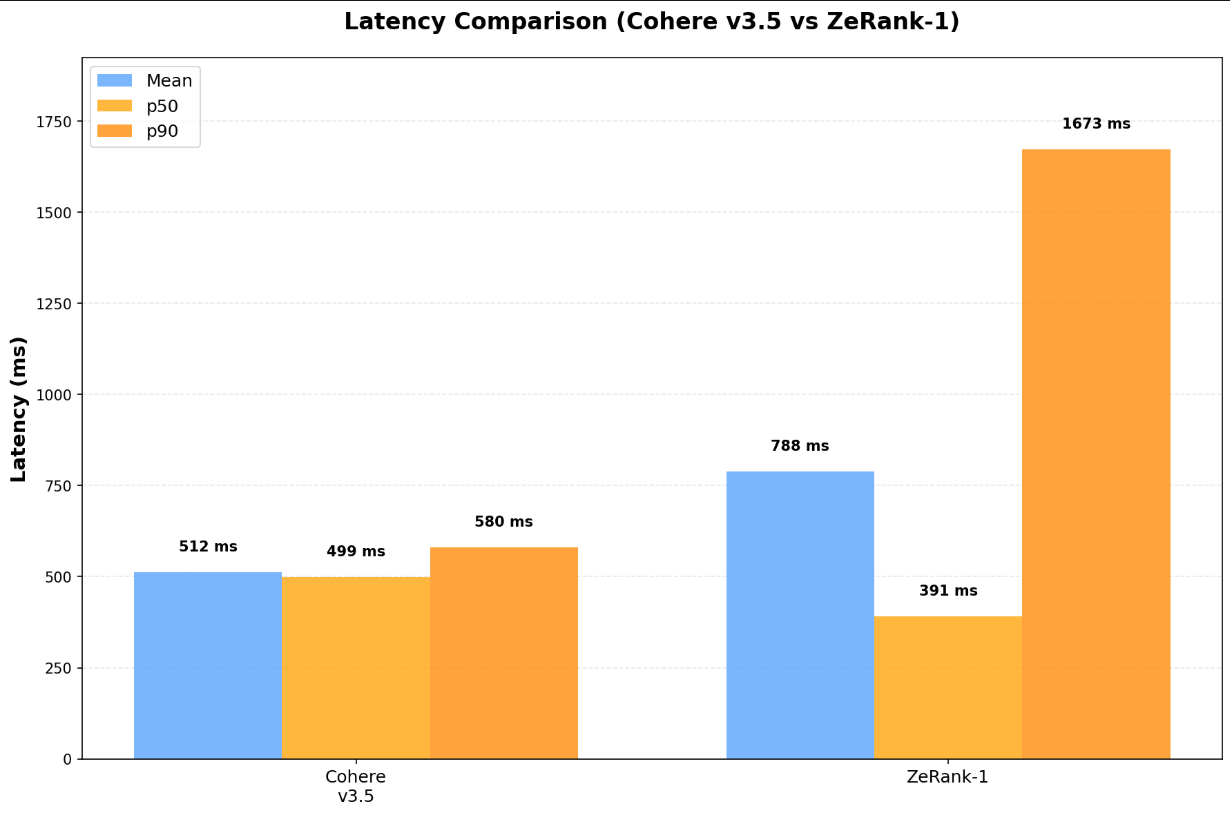
When comparing top-5 results per query, GPT-5 favored ZeRank in 39 out of 50 cases, a clear signal that its scoring better matches how an LLM interprets relevance.
How We Tested
To compare both rerankers fairly, we ran them through the same RAG setup in four stages.
Embedding: All documents and queries used BAAI/bge-small-en-v1.5, a compact bi-encoder with strong retrieval accuracy and low cost.
Retrieval: Top-50 candidate documents per query were retrieved via FAISS cosine similarity, forming the input for RAG reranking.
Reranking: Both rerankers received identical query-candidate sets. Requests ran asynchronously (four per model) to simulate parallel RAG workloads. We logged latency, status, and the top-15 results for every query on both datasets.
LLM preference: We asked GPT-5 to compare the top-5 results from each reranker for every query and pick which list was more relevant.
The Takeaway
Overall, ZeRank showed stronger relevance and responsiveness, while Cohere remained more stable under load. In the end, accuracy mattered more than speed.
Explore the code on GitHub
